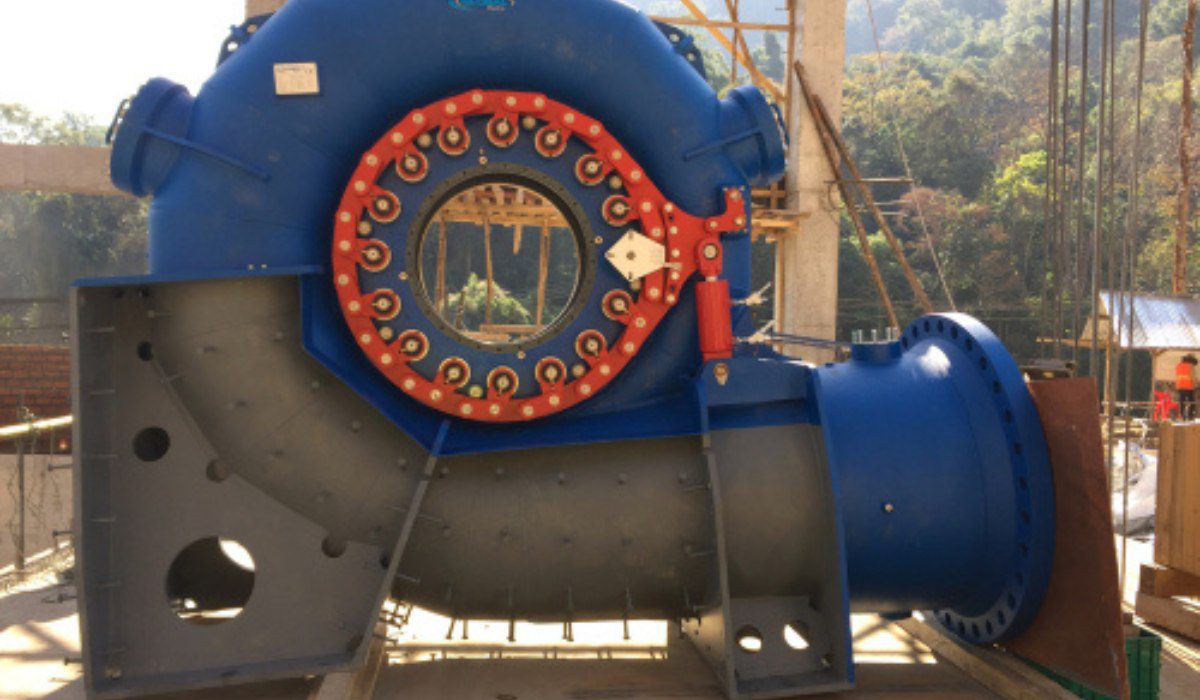
Turbines are effective equipment for producing hydropower on a large scale. Among all turbines, the Francis turbine is widely used, which is a kind of mixed turbine. Francis turbine is employed to convert kinetic energy into hydroelectric power. For approximately 135 years, the industry-based power production field has utilised this modern water wheel to get electricity.
In the year 1848, a British American senior engineer James B. Francis designed and invented this turbine design. James B Francis was the senior engineer of the Locks and Canals Company. He started to imply all kinds of mathematical and graphical measurement systems to match the higher efficiency level of a turbine. Read on to learn more about Francis turbine and its applications, advantages and disadvantages.
know about: different type of valves
Francis turbine: What is it?
Francis turbine is a mixed turbine which is a very complicated design of impulse turbine and reaction turbine. In this turbine, there are some runner blades which make use of reaction force along with the impulse force of flowing water. This turbine is used to produce electricity rapidly, and the usage of the Francis turbine is usually seen in large-scale hydropower stations.
Francis turbine: Components
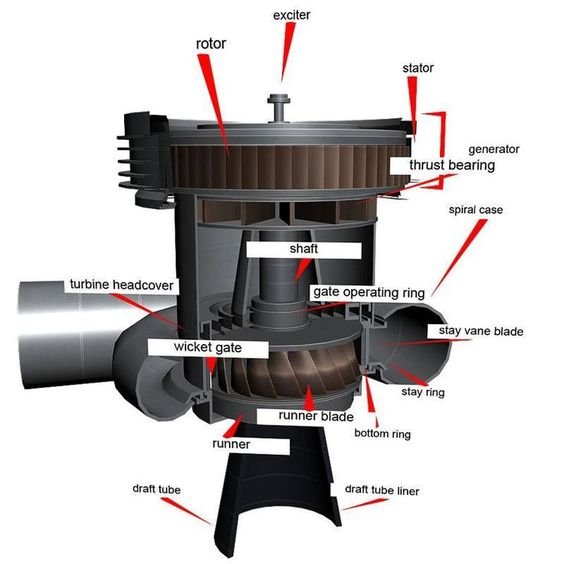
Francis turbine consists of five major components. These include:
Spiral casing
The spiral casing is the innermost area of a turbine which works as a medium of water. Water flows in high pressure inside this casing. In the casing, a few blades are situated in a circular way. For this arrangement, water flows according to a circular axis. As there is a circular movement, usually it may happen that pressure is reduced, but to keep the pressure constant, the diameter of the casing is reduced gradually.
Stay vanes
These are known as the guide of water to the blade of the turbine. Usually, stay vanes are fixed, and it reduces the water swirling system. They are helpful in making the turbine more efficient.
Guide vanes
Guide vanes are not fixed inside the turbine, and it changes the angle according to the needs of the control of the angle. Guide vanes are also helpful in controlling the water flow rate.
Runner blades
These are the most important parts because they are responsible for the efficiency of the turbine. There are two parts to the runner blades. The lower part is designed like a small bucket shape which employs the impulse action of water. The upper part works with the reaction force of water flow.
Draft tube
Usually, the pressure of the draft tube is lower than normal air pressure. From this tube, water can not exit directly.

Source: Pinterest
See also: I-beam: What is its use in the construction industry?
Francis turbine: Working principle
Francis turbine is a reaction turbine. In this turbine, water comes to the turbine pipe under heavy pressure. The energy from this turbine is released from water by the turbine blades. Inside the turbine blades, pressure changing takes place. This is known as the degree of reaction.
Another part of the whole energy is released by the volute casing of the turbine pipe. When it is time to exit the water, water goes through the cup-shaped runner. This runner creates a lower range of velocity and a lower range of swirl. This swirl comes with a very small potential energy. The exit tube or water discharge lowers the water flow pressure.
Source: Pinterest
See also: What is retrofitting in the construction industry?
Francis turbine: Efficiency
The efficiency and performance of a Francis turbine depend on the design of its runner blades. In this turbine, the runner blades are split into two parts. The upper half of these blades use the reaction force of the water flowing through the turbine whereas the lower half is shaped like a small bucket and uses the impulse action of water. These two forces combine to make the turbine rotate.
To ensure efficiency, it’s essential for water to reach all the blades equally. The flow of water is controlled by a casing that curls around the Francis turbine in a spiral shape. The spiral casing feeds water into the turbine rotor’s moving blades through a set of fixed blades and valves. When designed correctly, a Francis turbine can capture around 90% to 95% of the energy present in the water.
Francis turbine: Applications
Francis turbine has some serious applications such as:
- The most common application of the Francis turbine is in hydro-power plants to generate electricity.
- It is also used in irrigation water pumping sets for pumping water from ground for irrigation.
- The Francis turbine is designed to achieve a higher efficiency rate.
- In various pumped storage, this turbine is used to fill the reservoir.
- Francis turbines can be employed for a higher range of flows.
See also: About Kaplan turbine
Francis turbine: Advantages
- Usually, there is no head failure, even if the water discharge level is lower.
- The mechanical efficiency rate is quite higher than any other turbine.
- The runner size is competitively smaller than other turbines.
- Head control can be regulated easily.
All about: Automation in construction: How it will help developers and end-users
Francis turbine: Disadvantages
- The runner of the turbine is not always easily available.
- Francis turbine always demands costly maintenance.
- There is a possibility of cavitation.
- The design of the Francis turbine is complex.
- The cost of the Francis turbine is higher.
Francis turbine: What is cavitation?
Cavitation is a major problem faced by hydraulic machines. It adversely affects their performance and can also cause damage. Cavitation refers to the phenomenon that occurs in the pitting of the turbine’s metallic surfaces due to cavity formation. Here are some forms of damage that can be caused by cavitation in a Francis turbine:
- Distortion of blade angle
- Erosion of material in turbine parts
- Efficiency losses due to erosion or distortion
How to avoid cavitation in Francis turbine?
To avoid cavitation in Francis turbines, various strategies can be implemented:
- Submerged Runner: Keeping the runner or turbine submerged underwater is an effective method to steer clear of the cavitation zone. This ensures that the runner remains consistently submerged, minimizing the risk of cavitation.
- Low Specific Speed Runner: Utilizing a runner with a low specific speed contributes to cavitation prevention. By selecting a runner design that aligns with specific speed requirements, the turbine can operate without encountering cavitation issues.
- Design Optimization: Designing a cavitation-free runner necessitates in-depth research and optimization. Carefully engineering the runner to meet specific conditions can effectively prevent cavitation.
- Surface Polishing: Reducing cavitation effects can be achieved by polishing the runner’s surface. Coating cast steel runners and blades with stainless steel enhances their resistance to cavitation.
- Material Selection: Opting for materials with superior resistance to cavitation can mitigate its effects. Cast steel is preferable over cast iron, and materials like stainless steel or alloy steel provide enhanced resistance against cavitation.
- Proper Specific Speed: Selecting a runner with the appropriate specific speed for the given head is crucial in preventing cavitation. Ensuring a proper match of specific speed promotes smooth turbine operation without encountering challenges related to cavitation.
FAQs
What is the major application of the Francis turbine?
Francis turbine is mainly used in hydroelectric power plants, and high pressure of water passes through the turbine.
Are Kaplan and Francis turbines different?
Yes, both are different. The Francis turbine is a mixed hydraulic turbine, and on the other hand, the Kaplan turbine is an axial hydraulic turbine.
What are the three major steps of the turbine?
Three major steps in any turbine are pressure staging, reaction staging, and velocity-compound staging.
What are various turbine engines?
Usually, four turbine engines are there: Turbojet, Turboprop, Turbofan, and Turboshaft.
Who invented the Francis turbine?
Francis turbine was invented by James Bicheno Francis, who was the senior engineer of the Locks and Canals Company.

Dhwani is a content management expert with over five years of professional experience. She has authored articles spanning diverse domains, including real estate, finance, business, health, taxation, education and more. Holding a Bachelor’s degree in Journalism and Mass Communication, Dhwani’s interests encompass reading and travelling. She is dedicated to staying updated on the latest real estate advancements in India.
Email: [email protected]











