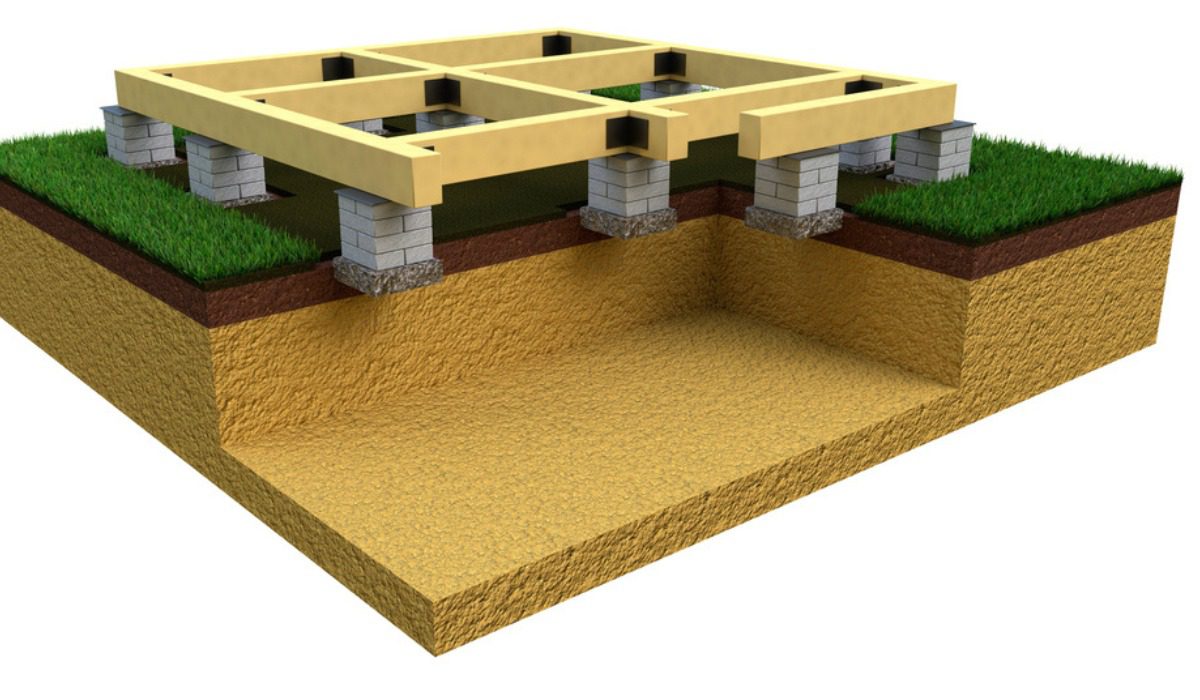
It is necessary to develop a building’s foundation so that the weight of the building’s framework may be distributed evenly over the ground. When single columns are spaced far apart, one of the most common forms of foundation that is used is an isolated footing since it is able to sustain the weight of the individual columns. In this article, know about isolated footing, including its design, benefits and everything else associated with it.
What is isolated footing?
Isolated footings are one example of a shallow foundation. Used for supporting and dispersing point loads, such as those produced by columns or pillars, they are a popular addition to shallow foundations. It is acceptable to use either reinforced or non-reinforced materials for isolated footings. Non-reinforced footings, on the other hand, need a greater footing height to provide the same load-spreading effects.
Separate columns are propped up by the isolated footing. They might have a flat base or protrude from the concrete to provide a steeper angle. In most cases, the concrete bed will have a 15 cm offset on all sides. Brick masonry columns have a 5 cm offset built into each of their four sides at frequent intervals along the course of the layers. In cases when slab, steeped, or slope footings for concrete columns are appropriate.
See also: Concrete slab: An essential element for construction
Types of isolated footing
There are different types of isolated footing. These include:
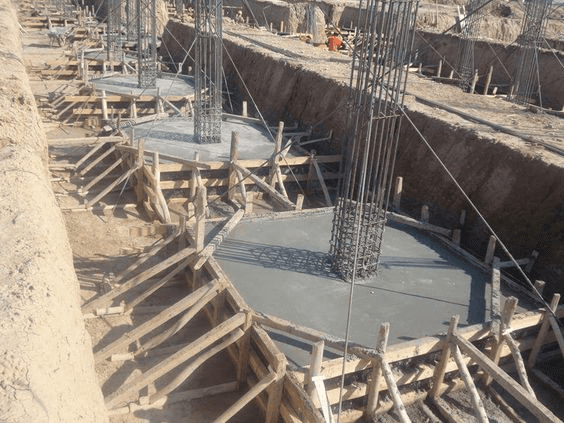
Flat or plain footing
Source: Pinterest
It is often made in a rectangular, square, or circular pattern, and it is constructed individually beneath each column. A uniform thickness characterises the flat isolated footing. It is incorporated to help reduce the shear stresses and bending moments at crucial spots in the structure. It may be built of either regular concrete or reinforced concrete, depending on how much more weight it has to support in the end.
Sloped footing

Source: Pinterest
The use of less concrete and reinforcing bars is required for sloped isolated footing in comparison to pad footing. It is created carefully so that a 45-degree slant may be maintained from all angles. In order to prevent viscous contraction, the concrete mix that is utilised must have a high degree of stiffness.
Stepped footing

Source: Pinterest
Stepped footings, also known as trapezoidal footings, are painstakingly planned and constructed in order to sustain a top slope of 45 degrees on all sides. When compared to the building of a conventional isolated footing, the use of reinforcement and concrete in the development of a sloping footing is much lower. Because of this, there is a decreased need for both concrete and reinforcement.
Isolated footing: Shapes
Isolated footings come in three shapes. These include:
- Square isolated footing: With a square shape, this type of square footing is used on stable soil.
- Rectangular isolated footing: With a rectangular shape, this type of square footing needs to be built for a rectangular column.
- Circular isolated footing: With a circular shape, this type of isolated footing is required in case of circular columns.
Details of isolated footing reinforcement
It is just as crucial to do a thorough site investigation prior to placing a footing as it is during the structural design phase. The importance of ensuring the footing’s structural integrity is shown in its meticulous attention to detail. Detailing such as the minimum reinforcement needed, bar diameters, and allowable footing dimensions, as well as a cover-to-reinforcement ratio dictated by environmental factors, are all examples of proper reinforcement.
A footing’s primary reinforcement must be at least 50 millimetres thick if it will be in touch with the ground. However, for surfaces that will be open to the environment, such as surface levelling PCC, the primary reinforcement should be at least 40 millimetres thick.
Learn more about the importance of Shallow foundation in construction
Designing isolated footings for specific loads
When designing an isolated footing, there are a few things to keep in mind, including:
- Determine the space required for the footings by utilising the calculated loads.
- Take into account an appropriate thickness for the footing.
- Compute the flexure critical section as well as the shear critical section.
- Perform the calculations necessary to determine the bending moment as well as the shear stresses in the tangential direction.
- Investigate the extent of the predicted layer’s thickness.
- Investigate the specifics of the reinforcement, and check that there are no bearing stresses in the structure.
- Check to see how long the process of development will take.
- The weights on the footings, the soil’s safe bearing capacity (SBC), the concrete quality, and the steel strength are all taken into account throughout this process.
Advantages of isolated footing in construction
- The expense of constructing isolated footing is not very high.
- It is not difficult to construct isolated footing.
- There is a reduced need for excavation of the ground.
- There is no need for labourers with a high level of expertise.
Disadvantages of isolated footing
- The ground must be firm around the perimeter of the foundation of the construction.
- It is possible that it will be of extraordinarily massive size in order to accommodate the hefty weight.
- Due to the independent foundations, this architecture is susceptible to differential settling, which has the potential to cause structural damage to the structure.
FAQs
When is isolated footing employed?
Whenever a property boundary, another structure, or some other obstruction makes it impossible to install a continuous footing under a vertical support component, an isolated footing is utilised instead. Supporting the column with a separate footing helps prevent accidental harm to surrounding structures.
Which soil is good for isolated footing?
Isolated pad footings may be built on sandy soil. Again, the load-bearing capabilities, groundwater level, and depth of the load-bearing stratum determine the area and depth. Under each column, concrete pads are installed, and these are linked together through connecting beams.
Which foundation is utilised for weaker soil?
A grillage foundation may be used in the same manner as a deep foundation. Under-reamed piles come highly recommended when working with black cotton soil because they provide a stable foundation at a reasonable cost.
How do you determine isolated footing volume?
The thickness and form of the cross-section will be used to determine the volume of the object.
Housing News Desk is the news desk of leading online real estate portal, Housing.com. Housing News Desk focuses on a variety of topics such as real estate laws, taxes, current news, property trends, home loans, rentals, décor, green homes, home improvement, etc. The main objective of the news desk, is to cover the real estate sector from the perspective of providing information that is useful to the end-user.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/housing.com/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Housing
Email: [email protected]