Self-assessment tax (SAT) and advance tax are two ways in which taxpayers pay income tax to the government. A SAT refers to the amount a tax assessee pays after the Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) and advance tax is deducted. One must pay a self-assessment tax before filing income tax returns (ITR).
See also: Income tax assessment order: What is it and why is it issued?
What is self-assessment tax?
Self-assessment tax is the tax one is liable to pay after deducting the TDS and advance tax paid in a financial year. One pays self-assessment tax if there is any pending tax liability during the assessment year, after considering deductions and taxes paid, at the end of a financial year. One must pay self-assessment tax by submitting Challan 280.
Self-assessment tax: Points to remember
- The ITR filing process is incomplete unless the total tax amount is paid. An invalid submission of tax returns may result in a higher interest rate on the tax due and other penalties.
- There is no specific due date to pay the self-assessment tax. However, SAT payment must be made before ITR filing for the financial year to avoid the interest charged on
Self-assessment tax calculation
The individual taxpayer must evaluate the total taxable income, tax amount, deductions and exemptions to pay the self-assessment tax.
- Compute the total income, including salary, income through dividends, interest income, rental income, etc.
- Calculate the net taxable income by subtracting the tax deductions and exemptions from the total taxable income, including standard deduction, house rent allowance (HRA), health insurance premium and tax-saving investments, such as NPS and PPF.
- Assess the tax liability considering the net taxable income.
- From this amount, reduce paid taxes, such as TDS, advance tax, interest income, etc. The final amount would be the self-assessment tax (SAT).
Why should you pay self-assessment tax?
A self-assessment tax must be paid by individuals earning income from other sources. It helps eliminate inaccuracies related to one’s taxable income.
The tax must be paid in the following cases:
- When taxpayers fail to consider an income while paying advance tax.
- The deducted TDS amount is inaccurate.
- Salaried individuals may gain substantial income through investments, such as fixed deposits (FD) and mutual funds, unknown to the employer.
How to pay self-assessment tax online?
Taxpayers can visit the official portal of the income tax department at https://www.incometaxindiaefiling.gov.in and click on the ‘e-Pay tax’ option. They would be redirected to the NSDL website to complete the process.
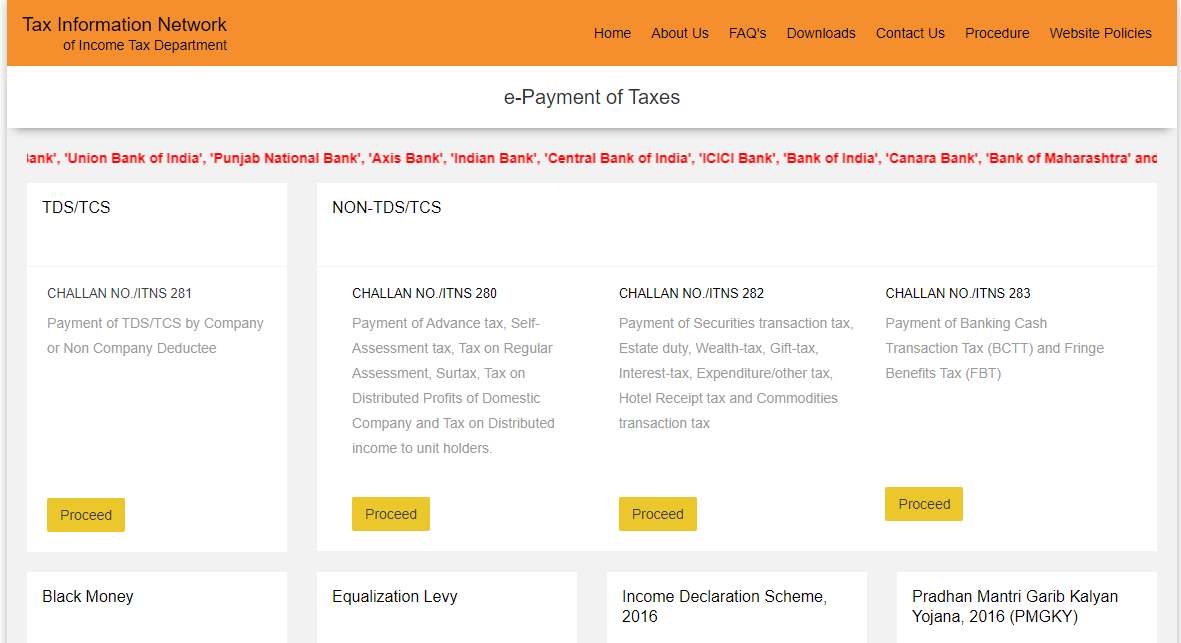
- Go to the Income Tax Department’s Tax Information Network portal https://onlineservices.tin.egov-nsdl.com/etaxnew/tdsnontds.jsp
- Select Challan number 280 (ITNS 280). Click on ‘Proceed’.
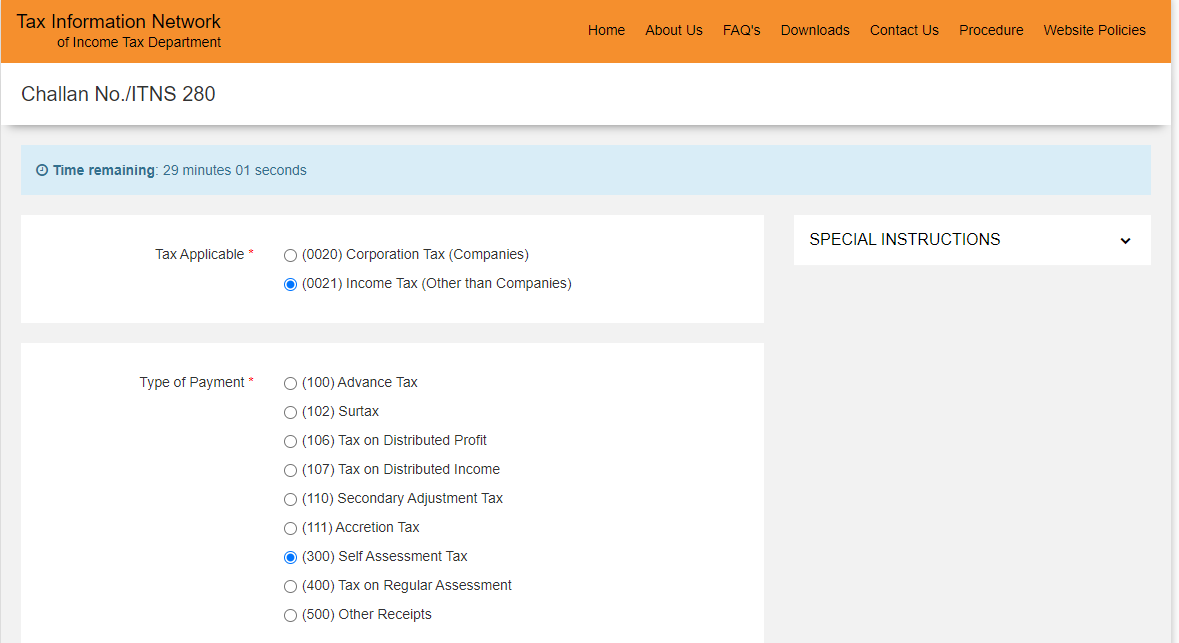
- On the next page, under ‘Tax Applicable’, select ‘(0021) Income-tax (other than companies)’. Click on ‘(300) Self-Assessment Tax’ under ‘Type of Payment’.
- Select the preferred payment mode – net banking or debit card.
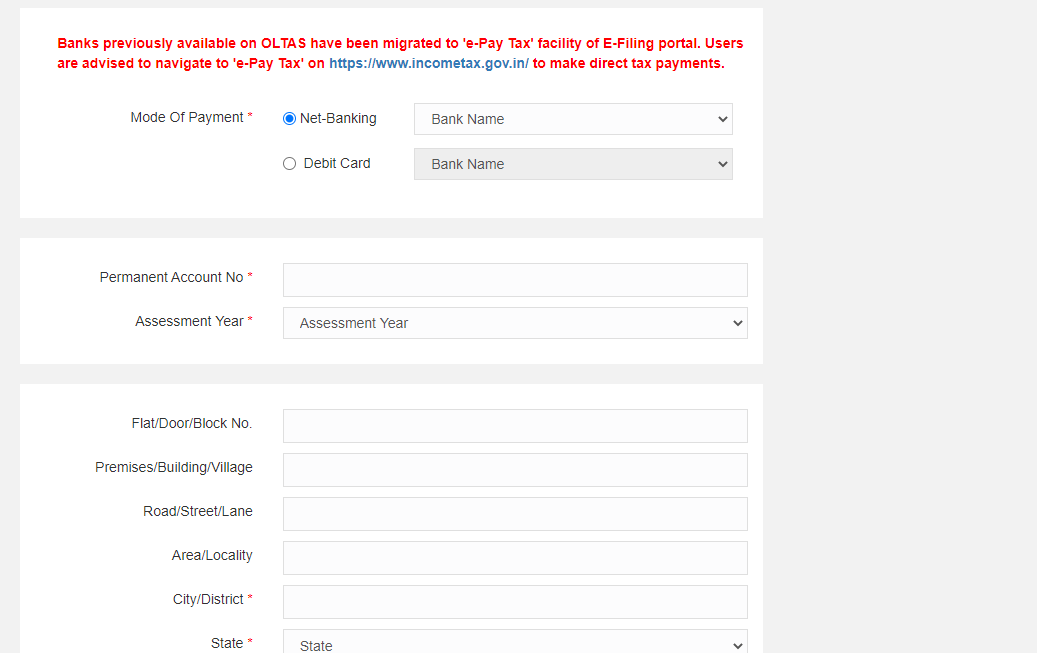
- The assessee must provide all the required details, fill in the captcha code and click on ‘Proceed’.
- After making the payment, download the challan.
The details of the self-assessment tax (SAT) payment will appear in Form 26AS.
How to pay self-assessment tax offline?
One can pay self-assessment tax offline by visiting their bank branch and following the below steps:
- Visit the bank branch to get the Challan 280 form
- Provide the required details as provided in the official TIN-NSDL portal
- Submit the duly filled Challan 280 form along with the money. The payment can be made in cash or through a cheque addressed to the ‘Income Tax Department’.
- The bank would accept the money and challan and provide a voucher.
FAQs
Is everyone required to pay the self-assessment tax?
Self-assessment tax must be paid by individuals for income from other sources. Self-employed people must pay the self-assessment tax if they have not considered a portion of their income when making the final payment or the TDS may not have been deducted.
Should the self-assessment tax be filed on a particular date?
The self-assessment tax must be paid before filing the income tax returns.
What is the difference between self-assessment tax and advance tax?
Advance tax is the part of one’s annual tax liability paid in advance, while self-assessment tax is the amount a taxpayer is liable to pay on their assessed income after deducting the TDS and advance tax.
| Got any questions or point of view on our article? We would love to hear from you.
Write to our Editor-in-Chief Jhumur Ghosh at [email protected] |
Harini is a content management professional with over 12 years of experience. She has contributed articles for various domains, including real estate, finance, health and travel insurance and e-governance. She has in-depth experience in writing well-researched articles on property trends, infrastructure, taxation, real estate projects and related topics. A Bachelor of Science with Honours in Physics, Harini prefers reading motivational books and keeping abreast of the latest developments in the real estate sector.











