In electrical devices and projects, connectors play a crucial function. Choosing the correct connection for the job is crucial. It is crucial for product efficiency and cost-effectiveness, as well as safety, PCB fabrication, and product production. As a result, manufacturers have developed a broad range of distinctive electronic connections that are specifically tailored to meet a product or application.
However, there are connections that are so adaptable that they are virtually certainly present in every electrical equipment used on a regular basis. So, this article will examine the type of connectors that are often used as well as their uses.
A pin header
Printed circuit boards are the main use for headers. These connections are widely accessible and quite affordable. Common in breakout boards, sensing modules, development boards, etc. With this, you can quickly connect any PCB module and unplug it whenever you want. Most low-voltage DC circuits in power and data lines employ header pins.
- Surface mount and through-hole (THT and THT) headers are likewise available.
- Headers come in two varieties: male and female.
- Its adaptability mostly results from its capacity to stack or unstack the header in accordance with our demands.
- It comes in a variety of pitch diameters, with 2.54 mil or 0.1 inches being the most popular.
- Frequently, headers are sold in the form of long strips with many pins that may be simply cut apart to the correct number of pins.

Source: Pinterest
The JST connector
In terms of use, they are somewhat comparable to pin headers, although they offer more benefits than straightforward headers. Two distinct boards or modules are connected using JST connections. Additionally used for power and data transfer, this connection.
- This is also available in male and female forms, with the male version commonly sitting on the PCB and the female version connecting to the peripheral device via an extended cable. In this situation, ribbon cables are often employed.
- It is protected from external pressure bending its tiny pins by being contained in a plastic container.
- For equipment with mechanical elements, this plastic enclosure also contains a locking mechanism that prevents the connectors from simply separating.
- The number of pins a JST connection has varies. Variants with 2, 4, 6, and 8 pins are often used.
![]()
Source: Pinterest
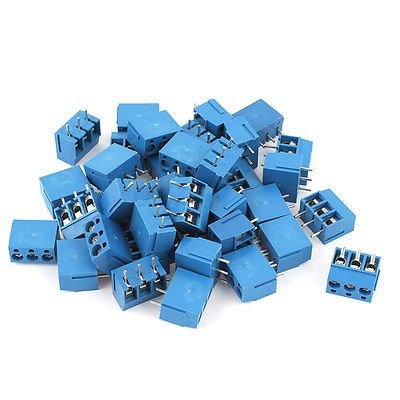
Screw terminal
Another form of connector is the screw terminal, which is mostly used to power PCBs. This connection is a useful power connector for both AC and DC applications since it can handle high currents and voltage with ease. This connector’s name comes from the screws that attach the wire connection to it. There are some excellent screw terminal options at this terminal retailer.
- While 4, 6, and 8 pin variants are also included on boards, the 2 pin type is the most typical.
- Plastic covers the real metal terminal to shield it from short circuits and other shock risks.

Source: Pinterest
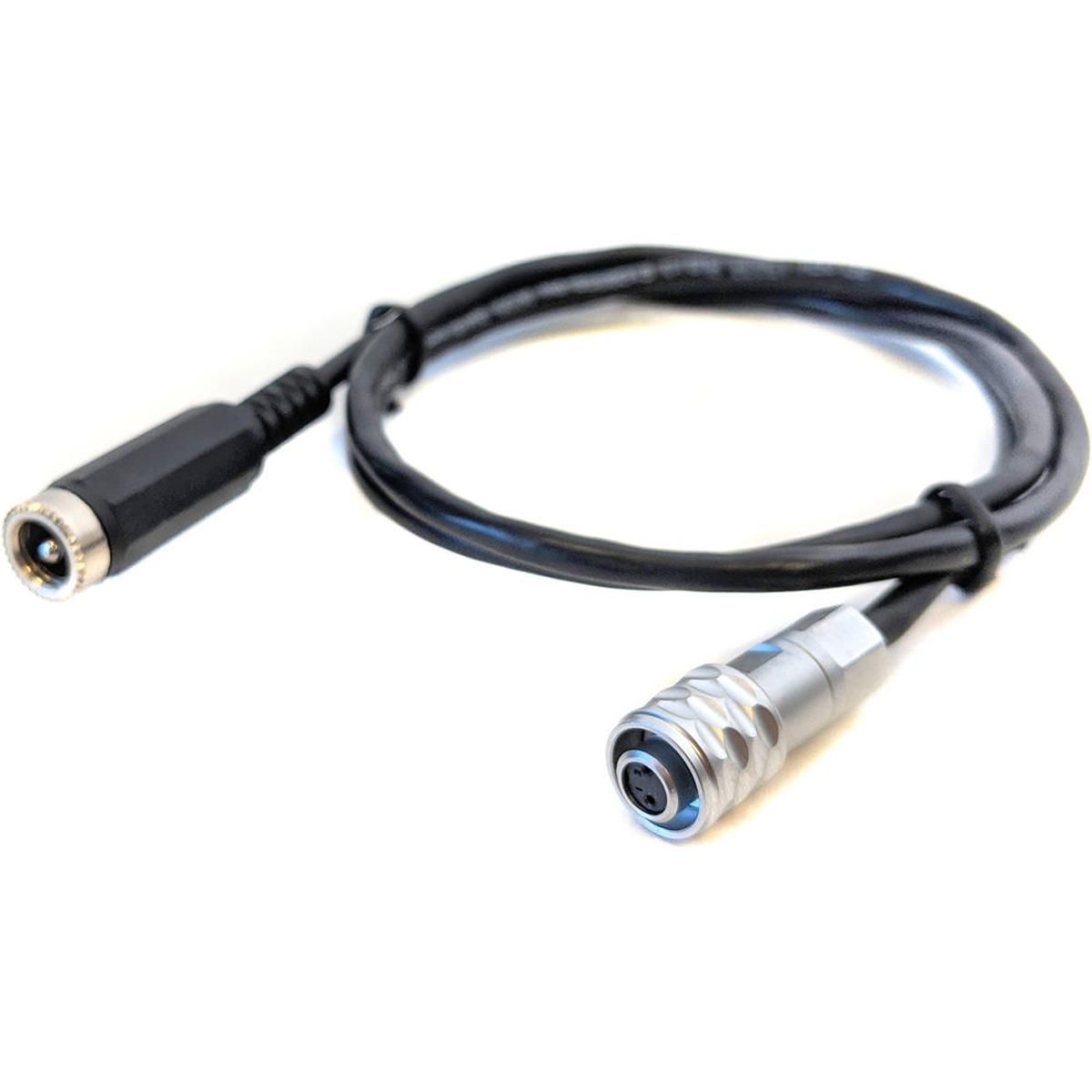
The barrels connector
A power connector known as a barrel connector is typically used with a DC supply, particularly wall adapters. The size of the male and female connectors should match for use because they have different diameters. This connection is well renowned for its user-friendliness because of the Tip and Sleeve arrangement that avoids misuse from users.
- There are PCB mount and non-PCB mount versions of it.
- To avoid inadvertent reverse connection, its cylindrical coaxial design was specially chosen.
- This connector’s sleeve is typically connected to the ground or the negative side of our power supply. The tip also connects to the power supply’s positive side.

Source: Pinterest
Connectors for cable lugs
These power connections are widely used. They come in a variety of sizes and shapes and sometimes with insulation. Control panels are often utilised in industrial applications due to their capacity to endure mechanical stress. Among the most well-known connection types are the Ring, Fork, Spade, and Butthead varieties.
- For creating secure connections, wires to these connectors are frequently soldered, crimped, or welded.
- These connections are available in a variety of thicknesses, and the maximum current they can carry depends on their size and the type of metal they are made of.

Source: Pinterest
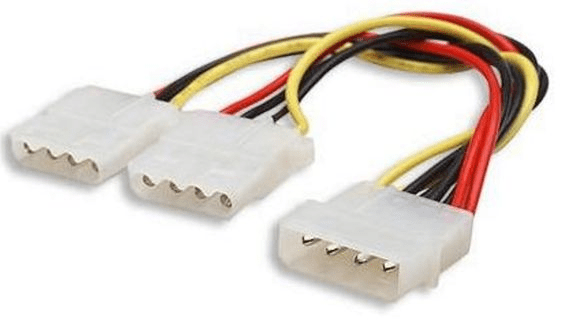
The Molex connector
Despite having a similar appearance to JST connections, Molex connectors often have larger pin pitches. They are frequently employed in power applications. Our PCs are one of the typical places to see this connection. You may have observed this in motherboards, hard drives, and other peripherals, as well as the ATX power supply unit of a computer.
- It has cylindrical spring-metal sockets and pins that fit into those sockets.
- A plastic casing is used to protect the pins and sockets.
- Depending on the application, a connector could have 2 to 24 contacts in a single or double-row arrangement.
- A polarity locking device protects the pins and sockets in a single enclosure to guarantee the right orientation.
Source: Pinterest
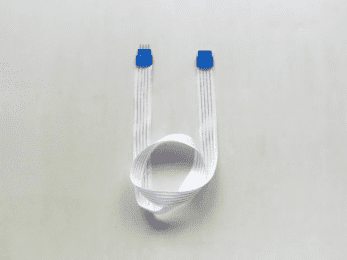
FFC: Flat flex connector
The connector’s light weight and increased flexibility are both crucial features. Most frequently found in modern electronics like mobile phones, laptops, cameras, displays, and other devices that require wire to be twisted and utilised in confined locations.
- On a flexible cable, this type of connection has a flat piece of conducting material.
- It is a scaled-down version of a typical ribbon cable designed for highly dense electronic applications.
- To facilitate insertion and offer strain relief, the cable ends will be thicker than usual.
Source: Pinterest
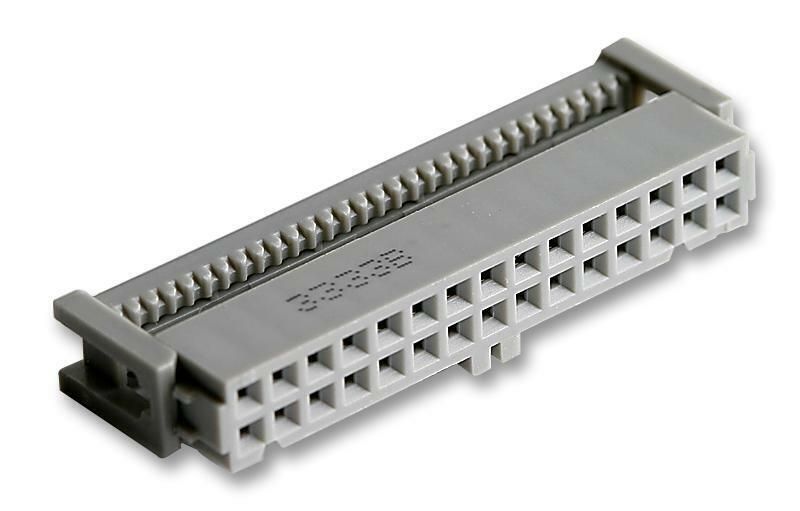
The IDC connector
When several parallel connections on a board need to be coupled, Insulation-Displacement connectors, or IDC connectors, are frequently used to transport data across boards. Most frequently seen in LCDs, networking and signal connections, etc.
- Made by forcing some pointed blades through a ribbon wire.
- IDC technology was ultimately expanded to link multiple stranded wires as well, despite being initially meant to simply connect single-stranded conductors in order to save up some mounting space.
- Comes with a locking mechanism as well to stop the cable from shifting or separating from the board.

Source: Pinterest
The RF connector
A unique kind of coaxial connector called an RF connector is utilised only in applications involving high-frequency radio waves. Applications that improve signal quality include WiFi antennas and TV signal receivers.
- A single core wire serves as the shield in this kind of connection by having many wires wrapped around it.
- Its coaxial construction minimises power losses and signal interference.

Source: Pinterest
Connectors for audio and video
Let’s briefly go over the most popular types of audio and video connectors because there are many other types available.
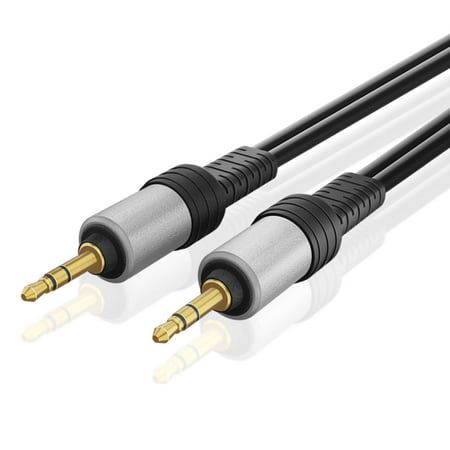
Connector for phones
Nearly all smartphones include what is known as a 3.5mm headphone port. Additionally, there are several sizes of this connection on the market.
- A common sight in our cell phones and other audio equipment.
- Supports audio output as well as input.
- Tip, ring, and sleeve coaxial connectors make up the typical 3 or 4 connections.

Source: Pinterest
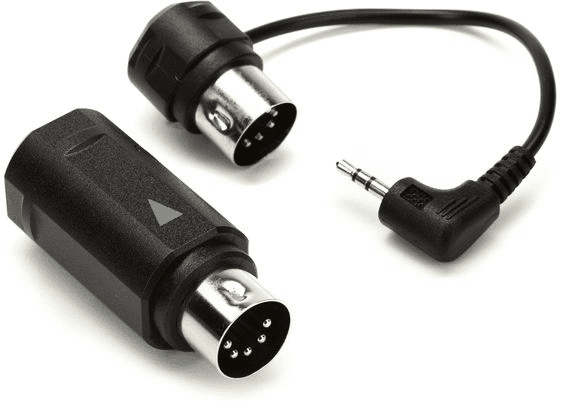
The DIN connector
For analogue audio transmissions, this particular kind of circular connector was first defined by DIN.
- A conductive ring surrounds three or more metal pins in a din connection.
- It contains a notch to restrict the plug and socket’s correct orientation.
- This kind of connection is typically utilised in analogue audio applications like MIDI devices and loudspeaker inputs.

Source: Pinterest
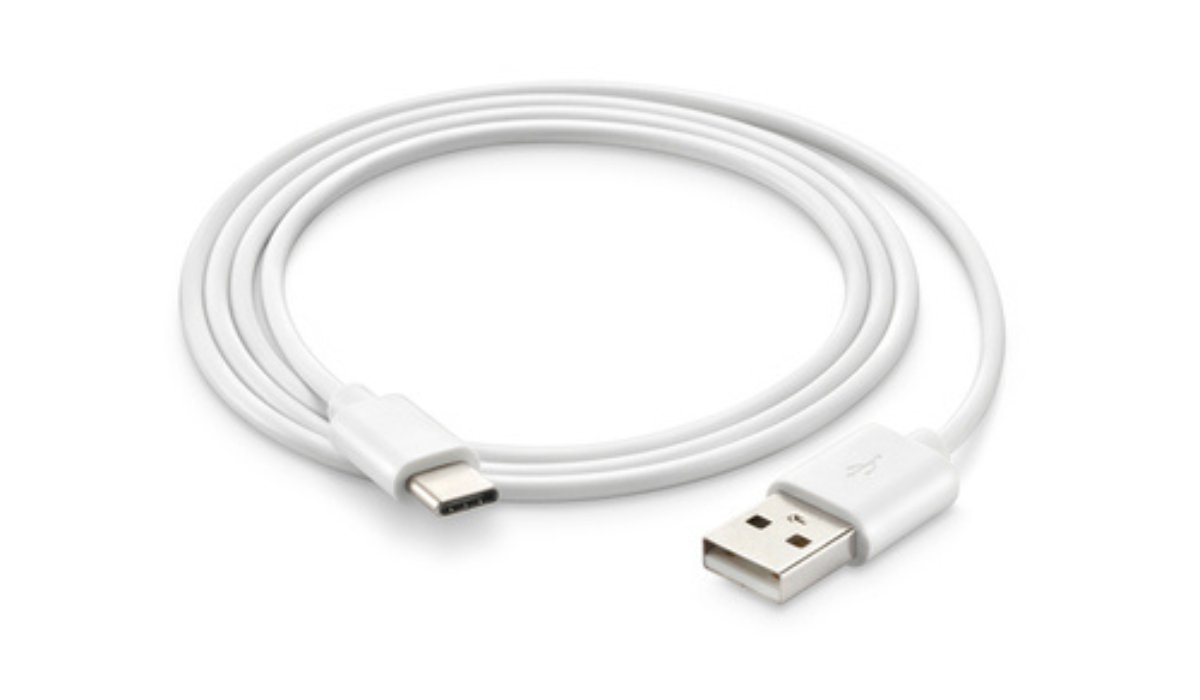
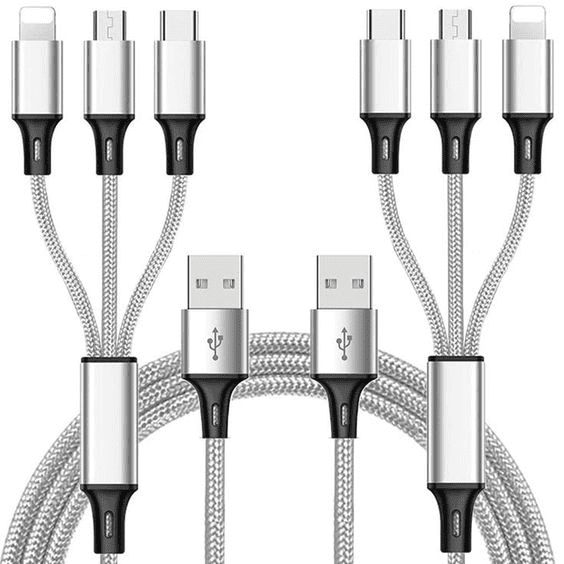
The USB connector
The standard protocol for connections for data transfer and power delivery is called USB, or Universal Serial Bus. Most prevalent in mobile phones, PCs, and other auxiliary equipment.
- 3 versions of USB have been developed: USB 1.x, USB 2.0, and USB 3.x.
- VCC, GND, DIN, and DOUT ports are always present on a conventional USB port.
- Works best with a voltage range of 5 volts.

Source: Pinterest
USB variants
Type A: Consumer electronics of type A include laptops and smartphones.
Type B: Printers and your trusty Arduino UNO are Type B devices.
Type C: The most recent version of this series is Type C. It is more potent, capable of sending data at a rapid pace and supplying the most power possible.
FAQs
Can connectors be used for both power and data transmission?
Yes, some connectors, such as USB and HDMI, are designed to transmit both power and data.
Are there connectors that are designed for specific types of devices?
Yes, some connectors, such as HDMI and USB, are specific to certain types of devices, such as televisions and computers.
Housing News Desk is the news desk of leading online real estate portal, Housing.com. Housing News Desk focuses on a variety of topics such as real estate laws, taxes, current news, property trends, home loans, rentals, décor, green homes, home improvement, etc. The main objective of the news desk, is to cover the real estate sector from the perspective of providing information that is useful to the end-user.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/housing.com/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/Housing
Email: editor@housing.com












